Nutrition has always been a topic surrounded by confusion. Every year, new diets, superfoods, and supplements claim to be the secret to health and longevity. In 2025, people are more health-conscious than ever, but myths about food still spread faster than facts. Misunderstanding nutrition can lead to unhealthy habits, wasted money, and frustration when results don’t match expectations.
This article breaks down common nutrition myths, explains the facts supported by science, and provides practical tips for building a balanced diet in today’s fast-changing world.
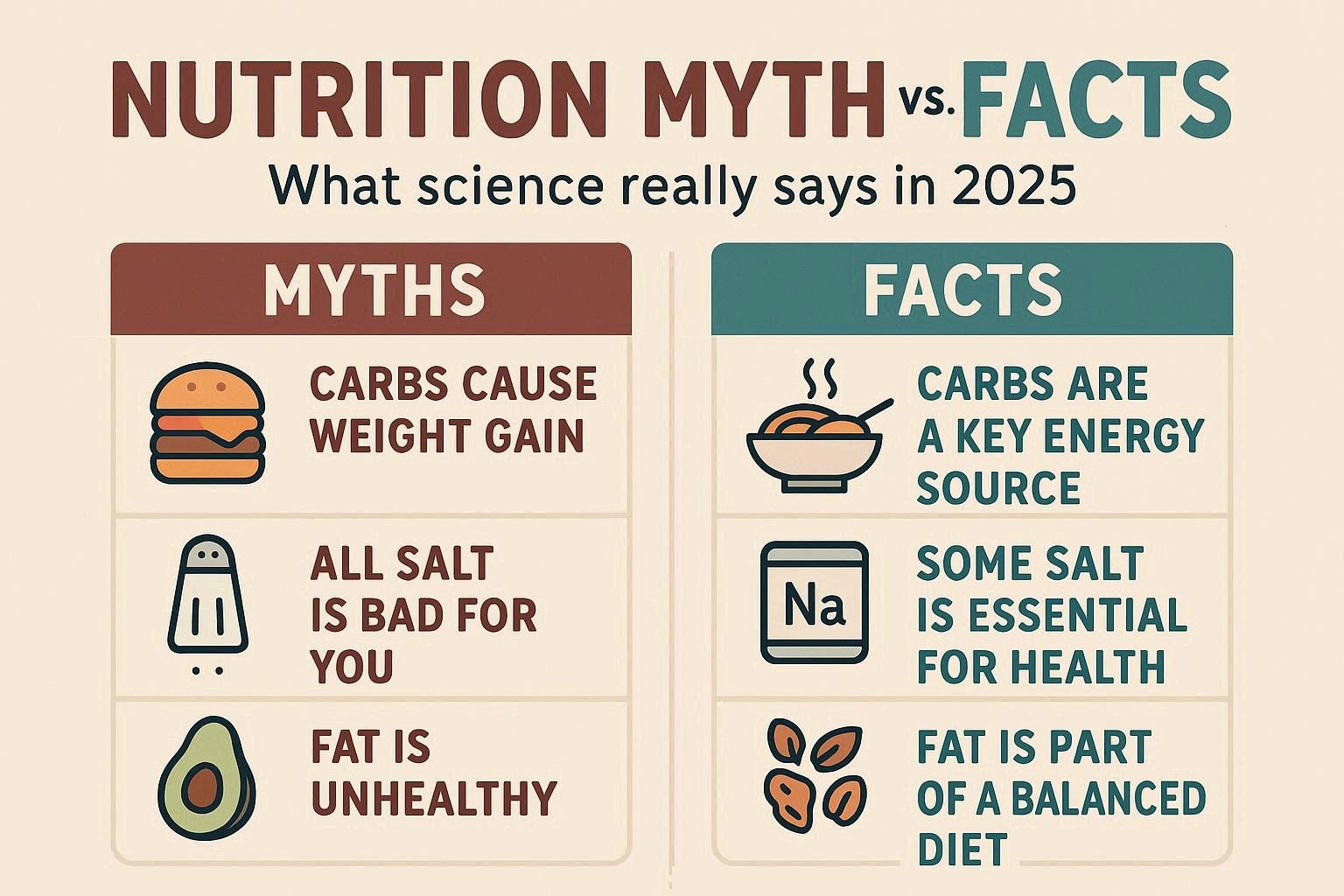
1. Myth: Carbohydrates Are Always Bad
The Fact: Not all carbs are the same. While refined carbohydrates like white bread, pastries, and sugary drinks can spike blood sugar levels, complex carbs such as whole grains, beans, fruits, and vegetables provide essential energy and nutrients. The key is choosing quality sources of carbohydrates rather than cutting them out completely.
2. Myth: High-Protein Diets Are the Only Way to Stay Fit
The Fact: Protein is important for muscle repair and overall health, but balance is essential. Excessive protein intake can put strain on the kidneys and crowd out other nutrients. A well-rounded diet that includes healthy fats, complex carbs, and adequate protein is the best strategy for long-term health.
3. Myth: Fat Makes You Gain Weight
The Fact: Healthy fats are crucial for brain function, hormone balance, and energy. Avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish provide unsaturated fats that support heart health. The real issue is trans fats and excessive saturated fats found in fried foods and processed snacks. Eating the right kind of fat in moderation is part of a healthy diet.
4. Myth: Supplements Can Replace a Healthy Diet
The Fact: Supplements can be helpful for filling specific nutritional gaps, but they should never replace whole foods. Vitamins and minerals are best absorbed from natural food sources because they come packaged with fiber, antioxidants, and other beneficial compounds. In 2025, experts recommend using supplements only when needed and focusing first on a balanced diet.
5. Myth: Skipping Meals Helps You Lose Weight
The Fact: Skipping meals often backfires by leading to overeating later in the day. Regular, balanced meals stabilize blood sugar, prevent extreme hunger, and support better energy levels. Intermittent fasting can work for some people, but it should be done with proper planning, not as an excuse for skipping meals randomly.
6. Myth: All Processed Foods Are Unhealthy
The Fact: Not all processed foods are bad. Freezing vegetables, for example, preserves nutrients, and fortified foods can help prevent deficiencies. The problem lies in ultra-processed foods—those high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats. Reading labels and choosing minimally processed options helps strike the right balance.
7. Myth: Detox Diets Cleanse the Body
The Fact: The human body already has a natural detox system—your liver, kidneys, lungs, and skin. Detox teas, juices, or restrictive diets are unnecessary and sometimes harmful. The best “detox” is simply staying hydrated, eating fiber-rich foods, and avoiding excess alcohol or processed junk.
8. Myth: Organic Food Is Always Healthier
The Fact: Organic foods are grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, which can be better for the environment. However, organic does not automatically mean more nutritious. A balanced diet made up of a mix of fresh, seasonal, and affordable foods—organic or not—can provide the nutrients your body needs.
9. Myth: Eating Late at Night Causes Weight Gain
The Fact: What matters most is the total number of calories consumed and the quality of food choices, not the time of day you eat. Late-night eating can contribute to weight gain only if it leads to excess calorie intake, often from snacks high in sugar or fat. If you are truly hungry at night, a small healthy snack is better than going to bed starving.
10. Myth: Superfoods Alone Can Transform Your Health
The Fact: Foods like blueberries, chia seeds, and kale are rich in nutrients, but no single food holds the key to perfect health. The real power lies in the overall pattern of eating—variety, balance, and moderation matter more than relying on a single “magic” ingredient.
11. Practical Tips for Healthy Eating in 2025
With so much conflicting information, it’s important to return to simple, science-backed principles:
- Prioritize whole, minimally processed foods.
- Balance meals with protein, complex carbs, and healthy fats.
- Practice portion control to avoid overeating.
- Stay hydrated throughout the day.
- Plan meals ahead to reduce reliance on fast food.
- Listen to your body’s hunger and fullness signals.
12. The Role of Technology in Nutrition
Technology plays a growing role in helping people make better dietary choices. In 2025, nutrition apps and smart devices track calorie intake, suggest healthier alternatives, and provide personalized diet recommendations. While these tools are helpful, they should be used as guides, not as replacements for mindful eating habits.
Conclusion
Nutrition myths have been around for decades, and while trends may change, the facts remain consistent. A healthy diet is not about extremes or quick fixes—it is about balance, variety, and sustainability. By understanding the truth behind common misconceptions, individuals can make informed decisions and create eating habits that support long-term health. In 2025 and beyond, the smartest approach is to keep it simple, stay consistent, and trust science over fads.